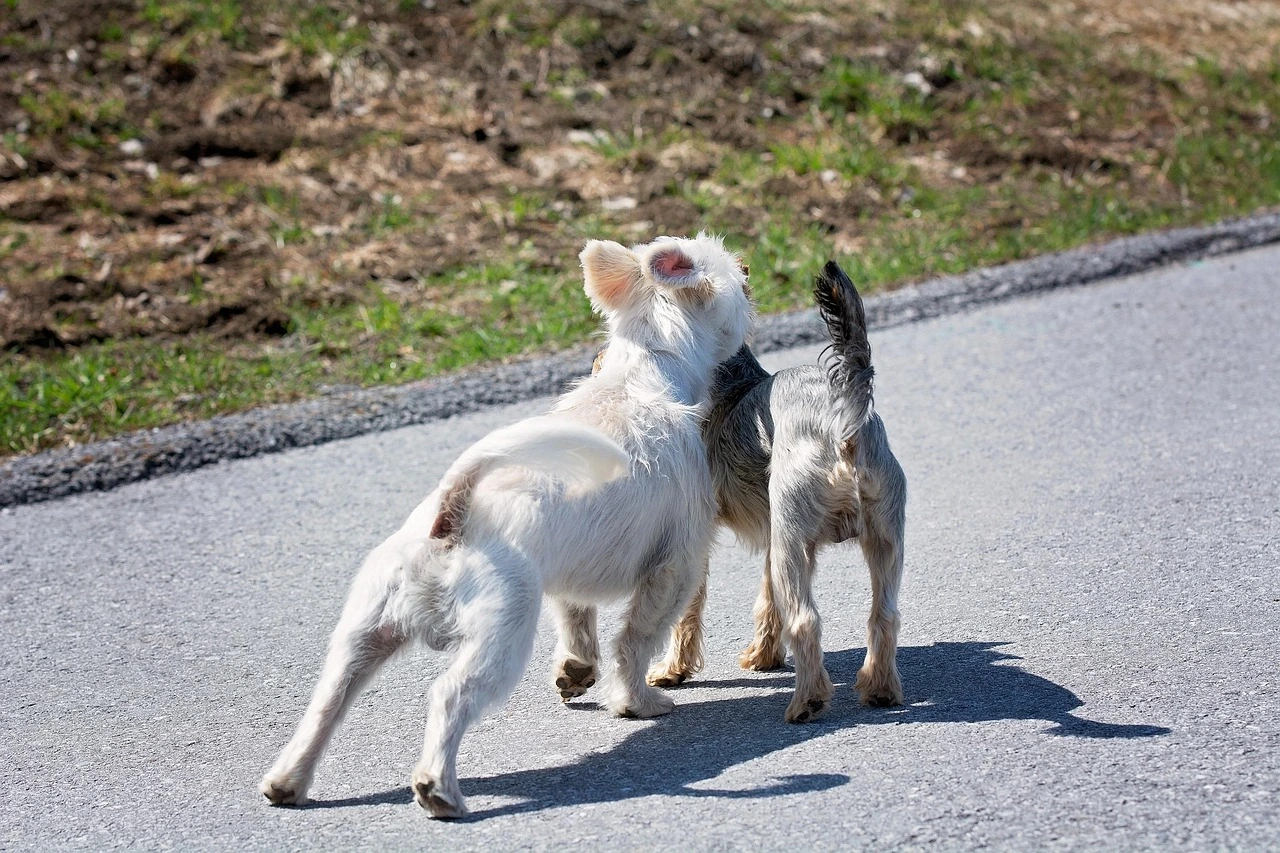
Why Do Dogs Get Stuck When Mating? Vet Answers Inside
Every dog owner has wondered about the mysterious process of canine reproduction. The reason dogs get stuck when mating is more interesting than you might think. Canine mating behavior is a complex biological process that can seem puzzling to even the most experienced pet owners.
Understanding why dogs get stuck when mating is crucial for responsible pet care. This natural phenomenon, known as “the tie,” is a completely normal part of the reproductive process for dogs. Our team of veterinary experts will guide you through the intricate details of this remarkable biological mechanism.
From the moment dogs begin their mating ritual, their bodies undergo a unique process that ensures successful reproduction. The tie is nature’s way of maximizing the chances of fertilization. It creates a temporary physical connection between male and female dogs that might look unusual to human observers.
If you’ve ever been curious about canine mating behavior or wondered about the science behind this remarkable process, you’re in the right place. We’ll break down the complex reproductive mechanisms and provide you with expert insights that demystify this natural phenomenon.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Canine Mating Process
Dogs have a complex mating process that is both fascinating and intricate. Their reproductive system is unique, unlike many other mammals. Knowing about these mating behaviors helps owners and breeders understand their pets’ natural cycles.
The mating process in dogs has several key stages. These stages are shaped by biology and the environment. They trigger specific behaviors in both male and female dogs.
Natural Phases of Dog Mating
Dogs follow a structured sequence in their mating rituals:
- Attraction and courtship
- Initial mounting
- Copulation
- The mating tie
What Happens During the Tie
Dogs experience a unique phenomenon called the “tie” or “knot” during mating. This happens when the male’s reproductive anatomy swells. It causes the two dogs to stay connected. The tie is crucial for successful reproduction.
| Mating Phase | Typical Duration | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Courtship | 15-30 minutes | Behavioral signals and mutual interest |
| Actual Mating | 5-10 minutes | Physical connection and reproduction |
| Mating Tie | 10-30 minutes | Physiological lock preventing separation |
Duration of the Mating Lock
The mating lock can last anywhere from 10 to 30 minutes. This ensures the best chance of successful fertilization. The dogs’ breed, age, and physiology can affect the tie’s length.
Understanding dog mating rituals helps owners appreciate their pets’ natural reproductive process. It also helps them recognize normal behaviors.
Why Do Dogs Get Stuck When Mating: The Scientific Explanation
To understand why dogs get stuck during mating, we need to look into their reproductive biology. This unique mating process is key to successful fertilization in dogs.
The male dog’s anatomy is crucial in creating the “tie” during mating. The bulbus glandis is a special part that swells during intercourse.
- The bulbus glandis expands inside the female’s reproductive tract
- This swelling creates a temporary biological lock
- The process prevents other males from mating with the female
This mating strategy is vital for canine reproduction. It ensures successful fertilization and prevents sperm loss.
- Maximizes the chance of successful fertilization
- Prevents sperm from escaping
- Ensures genetic continuation of the species
Hormonal changes trigger this complex process. When a female dog is in heat, her body sends out specific signals. These signals stimulate the male’s reproductive response. The tie usually lasts between 10-30 minutes, keeping the dogs connected.
| Mating Process Stage | Duration | Biological Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Mounting | 1-2 minutes | Positioning for Reproduction |
| Tie Phase | 10-30 minutes | Sperm Delivery and Retention |
| Post-Mating Separation | Varies | Natural Biological Disengagement |
This process might seem odd to us, but it’s a natural and essential part of dog mating. Nature has crafted this mechanism to ensure reproductive success in canines.
Female Dogs and Their Reproductive Cycle
Knowing how female dogs reproduce is key for pet owners and breeders. It’s important to understand the biological processes behind canine mating behavior.
The reproductive process in female dogs is both fascinating and unique. Veterinarians identify several stages that show a dog’s reproductive health and breeding potential.
First Heat Cycle Timeline
Female dogs usually have their first heat cycle when they become sexually mature. This age varies based on several factors:
- Small breed dogs: 6-9 months old
- Medium breed dogs: 9-12 months old
- Large breed dogs: 12-18 months old
Frequency of Heat Cycles
Most female dogs go through heat cycles twice a year. But, breed and individual traits can cause variations.
| Breed Size | Average Heat Cycle Frequency | Typical Cycle Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Small Breeds | 3 times per year | 2-3 weeks |
| Medium Breeds | 2 times per year | 2-3 weeks |
| Large Breeds | 1-2 times per year | 2-4 weeks |
Duration of the Estrus Phase
The estrus phase, when a female dog is ready to mate, lasts 7-14 days. During this time, your dog will show certain behaviors and physical signs that she’s ready to breed.
“Understanding your dog’s reproductive cycle helps ensure proper care and prevents unexpected pregnancies.” – Veterinary Reproductive Specialists
Watching your dog’s heat cycles helps you make smart choices about spaying, breeding, and managing her reproductive health.
Physical Signs of a Female Dog in Heat
Understanding how dogs mate means knowing the signs of a female dog in heat. These signs show your dog is ready to mate. It’s a natural part of their cycle.
The first sign is vulvar swelling. This change is subtle but clear. You’ll see your dog’s genital area getting bigger and slightly redder.
- Bloody vaginal discharge – this is the first sign most owners notice
- Swollen vulva with slight redness
- More frequent urination
- Behavioral changes
Your dog may act differently during this time. She might be more restless and attract male dogs. These changes are part of their natural mating rituals.
The heat cycle lasts 2-4 weeks. Your dog will attract male dogs more during this time. Her scent changes, drawing potential mates.
Pro Tip: Track your dog’s heat cycles to better understand her reproductive health and prevent unexpected pregnancies.
Watching for these signs helps manage your dog’s reproductive health. It helps you make smart choices about breeding or preventing it.
The Role of Male Dogs in the Mating Process
Learning about how dogs mate is really interesting. Male dogs have a big role in this process. They are driven by strong instincts during mating season.
Male dogs go through big changes when it’s time to breed. Their actions towards potential mates are complex. These changes are part of their natural breeding process.
Male Dog Behavior During Mating Season
Male dogs show special behaviors during mating season:
- They become more restless and alert.
- They have a strong urge to find mates.
- They mark their territory to show they’re ready to breed.
- They become very sensitive to female scents.
These behaviors are key to understanding how dogs mate. Male dogs can find females in heat from far away. They follow their scent.
Physical Changes in Male Dogs
Male dogs also go through physical changes during mating season:
- Their testosterone levels rise.
- They get more muscular.
- Their reproductive organs become more active.
- They might act differently.
These changes help male dogs prepare for breeding. It shows how complex canine mating behavior is. Knowing these changes helps pet owners manage their dogs better.
Safety Considerations During Dog Mating
Understanding dog mating is key for responsible owners. Why do dogs get stuck during mating? It’s a natural process that needs careful handling and safety steps.
Dogs form a unique reproductive bond called a tie during mating. It’s important to stay calm and not try to pull them apart. Forcing them apart can hurt both dogs badly.
- Never pull or force dogs apart during mating
- Keep the mating area quiet and stress-free
- Ensure both dogs are healthy and have been veterinary checked
- Supervise the entire mating process without direct intervention
Protecting both dogs during mating is crucial. Careful observation helps avoid problems from wrong handling.
“Patience is key during dog mating. Let nature take its course.” – Veterinary Reproduction Specialist
Having a vet watch can reduce risks. If you see signs of trouble or odd behavior, call your vet right away. They can offer advice tailored to your dogs’ needs.
| Safety Consideration | Recommended Action |
|---|---|
| Separation Attempt | Do NOT attempt to separate dogs manually |
| Environment | Create calm, quiet mating space |
| Health Screening | Verify both dogs are medically fit for breeding |
| Veterinary Consultation | Seek professional advice if complications occur |
Knowing these safety tips ensures a safe and successful mating for your dogs.
Common Misconceptions About Dog Mating
Understanding how dogs mate can be tricky for dog owners. Many people get confused about dog mating rituals. This leads to wrong ideas about breeding.
Many dog owners believe myths about how dogs reproduce. These myths can hurt your dog’s health and breeding chances.
Myths About First-Time Breeding
- Myth: A female dog must have at least one litter before being spayed
- Myth: First-time breeding guarantees easier subsequent pregnancies
- Myth: Young dogs always have trouble during their first heat cycle
Experts say these myths are not true. They suggest talking to professional breeders or vets for real advice on dog reproduction.
Truth About the Tie Process
Many people think a full tie is needed for successful mating. But, this is not always true.
Successful breeding depends on many things, not just the tie.
Here are some important facts about dog mating:
- Pregnancy can happen without a full tie
- How long mating lasts doesn’t mean conception
- Dogs can be very different in fertility
Knowing these facts helps dog owners make better choices about breeding and health.
Preventing Unwanted Mating and Pregnancy

Being a responsible pet owner is key in managing animal reproduction and controlling dog mating. To prevent unwanted dog pregnancies, you need to plan carefully and take action early.
The best way to stop unplanned breeding is through surgical sterilization. Spaying your female dog before her first heat cycle has many benefits:
- Eliminates risk of unplanned pregnancies
- Reduces potential health risks
- Decreases hormonal behaviors
If you’re looking for other ways to prevent breeding, there are some practical steps you can take:
- Keep female dogs indoors during heat cycles
- Use specialized dog diapers during fertile periods
- Separate male and female dogs when necessary
- Monitor your dog’s reproductive cycle closely
Vets suggest acting early to manage dog mating behavior. Talking to a vet can help you create a plan that fits your dog’s needs and health.
“Prevention is always better than cure in animal reproduction management.”
Remember, controlling breeding and population is crucial for your dog’s health and happiness.
When to Contact Your Veterinarian
Knowing when to seek vet help is key to understanding dog reproduction. Sometimes, your dog’s mating needs expert care for a safe and healthy outcome.
There are times when calling a vet is essential during dog mating. These moments are crucial to prevent problems for both dogs.
- Prolonged mating tie lasting more than 30-40 minutes
- Signs of distress or visible pain during or after mating
- Unusual bleeding or discharge post-mating
- Aggressive behavior between dogs during or after the reproductive event
Most mating ties are normal, but not all. Watch for signs that might mean you need vet help.
Vets are vital for reproductive health. They offer:
- Comprehensive reproductive health assessments
- Guidance on breeding practices
- Early pregnancy screenings
- Genetic health evaluations
Regular vet visits are key for breeding dogs. Your vet can monitor your dog’s cycle, spot health risks, and ensure safe breeding.
Professional veterinary care is the cornerstone of responsible dog breeding and reproductive health.
Conclusion
Knowing how dogs mate is key for pet owners. The process involves complex biology to ensure successful breeding. Learning about it helps support your dog’s health.
Canine mating is a natural process that needs attention and understanding. Each stage of the reproductive cycle is important for breeding. Knowing these details helps prevent health risks and ensures your pets get the care they need.
Vets are crucial when dealing with dog reproduction. They offer valuable advice, whether you’re breeding or just want to know more about your pet’s biology. Understanding how dogs mate helps you make better decisions for their reproductive health.
Being a responsible pet owner means knowing about your dog’s reproductive cycles. By understanding canine mating, you create a supportive environment for your pet’s health and well-being.







